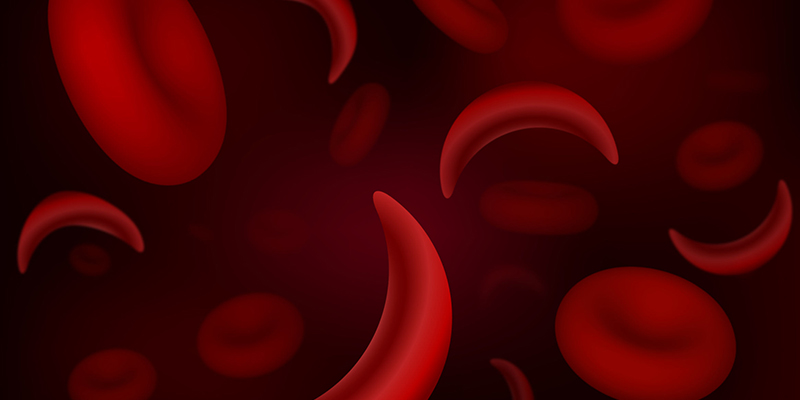
Sickle cell disease is a group of hereditary disorders of the red blood cell. People suffering from sickle cell disease have an unusual protein in their RBCs. In this disease, the red blood cells are not shaped as they should be. Normally, RBCs look like round discs, but in sickle cell disease, they’re shaped like crescent moons, or an old ranch instrument known as a sickle, thus the name being-Sickle Cell disease.
These sickle shaped cells get accumulated and entangled together very easily and, block off smaller blood vessels as a result of which, blood can’t go where it should thus leading to pain and organ damage.
Signs & Symptoms of Sickle Cell Disease
People suffering from sickle cell disease can have pain when blood can’t get to parts of the body resulting into a condition called pain crises.
Pain may be felt in any part of the body and may be triggered by cold, stress, illness, or dehydration. The pain may be experienced for few hours, days, or sometimes even longer. Sometimes pain can be managed at home. But someone with severe pain might need hospital care.
People with sickle cell disease often have a low count of red blood cells, or anemia. Signs of anemia include:
- Paleness, (evident from skin, lips, or nailbeds)
- tiredness
- dizziness
- being short of breath
- feeling lightheaded
- being irritable
- trouble paying attention
- a fast heartbeat
People suffering from sickle cell anemia may have jaundice (skin and whites of the eyes look yellow). This happens because the sickle-shaped red blood cells break down faster than normal RBCs.
Complications associated with sickle cell disease
People with sickle cell disease can have problems that might need immediate medical assistance, such as:
- Acute chest syndrome:Caused by inflammation, infection, and blockages of small blood vessels of the lung. Signs include chest pain, coughing, trouble breathing, and fever.
- Aplastic crisis: This happens when the body temporarily does not make enough red blood cells, resulting in severe anemia.
- Infection: People with sickle cell disease are at an increased risk for some bacterial infections. It’s important to watch for fevers of 101°F (38°C) or higher, which can be signs of an infection.
- Priapism: Men with sickle cell disease can have painful, long-lasting erections.
- Stroke: Sickle-shaped cells can block small blood vessels in the brain, resulting a stroke. Signs can include headache, seizure, weakness of the arms and legs, speech problems, a facial droop, or loss of consciousness.
Also, individuals suffering from sickle cell disease are prone to problems such as leg ulcers, bone or joint damage, gallstones, kidney damage, eye damage, and delayed growth.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
The only known cure for sickle cell disease is Stem cell transplant (also called bone marrow transplant). However, transplants are complex and risky procedures, and for now are an option only for some patients.
Researchers are working on gene therapy as a treatment for sickle cell anemia. It is hoped that changing or replacing the abnormal gene can heal the patient.
But even without a cure, individuals with sickle cell disease can lead normal lives following their treatment plan which involves:
- Immunizations: Including all recommended childhood vaccinations also, in sickle cell disease, daily doses of penicillin is recommended to help prevent infection.
- Regular intake of folic acid supplements to help them make new red blood cells.
- Intake of hydroxyurea, a medicine that makes sickled red blood cells less sticky so that clusters of cells are not formed and less episodes of pain happen. Hydroxyurea needs to be taken on a daily basis.
- Painkillers to help bear painful crises
- Blood transfusions
Trivitron Healthcare Offers advanced health technologies for better analysis of blood disorders
Minicap Flex Piercing – The fully automated instrument meets the needs of the laboratory while providing clear-cut and precise separations utilizing the capillary electrophoresis technology. This multi-parametric instrument with 2 capillaries offers a comprehensive menu on serum and whole blood for Protein, immunotyping, HbA1c, Hemoglobin, CDT (Carbohydrate Deficient Transferrin) testing.
Capillarys 3 Octa / Tera – Multiparametric stand-aloneinstruments with 8/12 capillaries in parallel. A proven analytical excellence meets high throughput and offers a broad assay menu: Serum Protein, immunotyping, HbA1c, Hemoglobin, CDT (Carbohydrate Deficient Transferrin) testing.

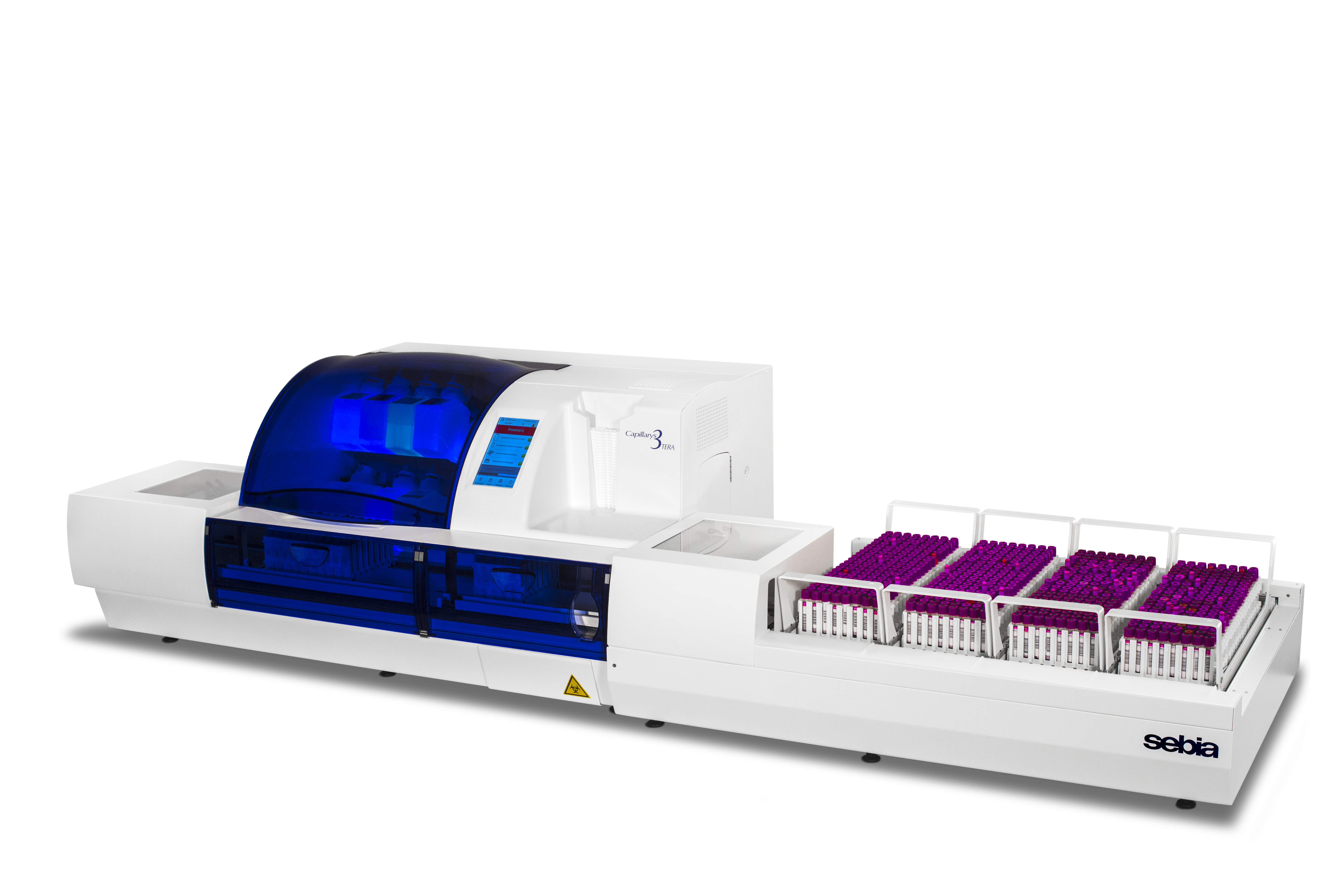
Capillarys2 Neonat Fast – Is the best choice in Newborn Hemoglobin Screening on dried Blood Spot. Exclusive capillary electrophoresis technology for high resolution separation and complete walk-away automation, from hemolysate preparation to final color-coded results.