Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder. People with Thalassemia disease are not able to make enough hemoglobin, which causes severe Anaemia. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells and carries oxygen to all parts of the body. When there is not enough hemoglobin in the red blood cells, oxygen cannot get to all parts of the body. Organs then become starved for oxygen and are unable to function properly.
There are two primary types of Thalassemia disease:
- Alpha Thalassemia disease
- Beta Thalassemia disease.
Alpha-thalassemia
Alpha thalassemia refers to a group of disorders characterized by inactivation of alpha globin genes. This results in a relative increase in nonfunctional beta globin or gamma globin tetramers and subsequent cell damage. Normally, there are four alpha genes. Absence or non-function of three alpha genes results in hemoglobin H disease, and the loss of all four alpha genes usually results in intrauterine death.
The alpha thalassemias are caused by a decrease in production of alpha globin chains due to a deletion or mutation of one or more of the four alpha globin genes located on chromosome 16.
The alpha thalassemias can be generally categorized as:
- Silent Carrier,
- Alpha Thalassemia Trait,
- Hemoglobin H disease,
- Hemoglobin H-Constant Spring, and
- Alpha Thalassemia major.
Beta-thalassemia
The beta thalassemia is much more diverse than the alpha thalassemia syndromes due to the diversity of the mutations that produce the defects in the beta globin gene.
Unlike the deletions that constitute most of the alpha thalassemia syndromes, beta thalassemias are caused by mutations on chromosome 11 that affect all aspects of beta globin production: transcription, translation, and the stability of the beta globin product.
Most hematologists feel there are three general categories of beta thalassemia:
- Beta thalassemia trait,
- Beta thalassemia intermedia
- Beta thalassemia major.
Thalassemia Symptoms
There are several types of thalassemia. The signs and symptoms you have, depends on the type and severity of your condition.
Thalassemia signs and symptoms can include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Facial bone deformities
- Slow growth
- Abdominal swelling
- Dark urine
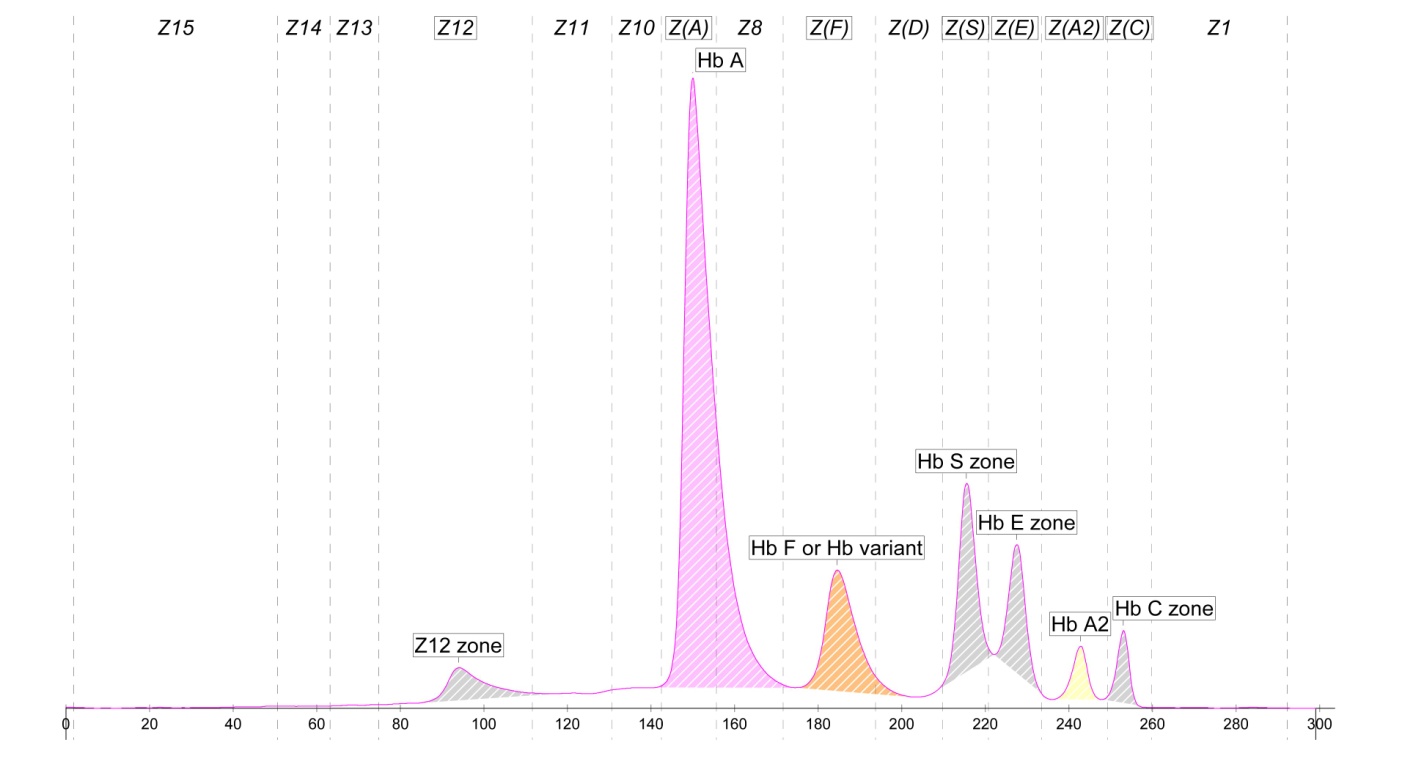
DIAGNOSIS BY CAPILLARY TECHNOLOGY:
Capillary Electrophoresis technology is the latest technology for precise and accurate estimation of thalassemia and Hemoglobinopathy screening, which is accepted globally and included in the guidelines of many countries.
Capillary Electrophoresis technology provides better separation than any other technology. All the peaks are well separated from each other and avoids co-elution of two different variants specially HbE which is the major challenge.
Capillary Electrophoresis systems offer complete solutions for talassemia and Hemoglobinopathies, and make use of Adult whole Blood, Cord Blood and Dried Blood Spot as analytical samples.
Some of the most widely used Capillary Electrophoresis systems are:
Minicap Flex Piercing:Two Capillary Electrophoresis systems
Capillarys 3 OCTA: Eight Capillary Electrophoresis systems
Capillarys 3 TERA: Twelve Capillary Electrophoresis Systems
Capillarys 2 Neonat Fast: Eight Capillary Electrophoresis system dedicated for Neonatal Hb screening